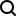Overview of the KDF-GAC-Poly Phosphate & Alkaline Filters
KDF-GAC-Poly Filtration
KDF media is used in place of, or in conjunction with, activated carbon which removes 99% of the chlorine taste and odor in municipal water by bonding to KDF media. KDF media also inhibits bacteriostatic, algae and fungi) by setting up an electrolytic field and also by forming peroxide and hydroxyl radical by Redox Reactions. GAC filtration is most effective in removing organic contaminants from water. Polyphosphate Media is added to mask the effects of high iron concentrations.
- Change Hardness Chemically for not to Corrode or Stick Inside Pipelines.
- Removes Hardness from Water.
- Bacteriostatic Media: Prevents Bacteria Growth.
- Improves Taste, Eliminates Odors.
- Improves Water Clarity.
- Provides Extended Filter Life.
- Lower total cost, Decreased maintenance and Improved Performance.
- Maximum Capacity 5,000 Gallons.
Kinetic Degradation Fluxion Media (KDF)
KDF Process Media are high-purity, granulated copper and zinc-based alloys that treat water and waste water through a process based upon the principle of redox (Oxidation-Reduction). Originally, KDF was shorthand for Kinetic Degradation Fluxion. KDF Process Media enhances the performance, extends the life, reduces the maintenance and lowers the total cost of carbon-based Media. KDF Process Media helps to control microorganisms by creating an environment that is deadly to some microorganisms, and that interferes with the ability of many other microorganisms to function. Either way, the use of KDF Process Media results in the total elimination of some contaminants, and a great reduction of a wide variety of others which will protect the RO Membrane elements from Fouling due to bacterial growth.
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
GAC filtration is most effective in removing organic contaminants from water. Organic substances are composed of two basic elements, carbon and hydrogen. Because organic chemicals are often responsible for taste, odor, and color problems, GAC filtration can generally be used to improve aesthetically objectionable water. GAC filtration will also remove any excess chlorine. GAC filtration is recognized by the Water Quality Association to maintain drinking water contaminants within the limits of the EPA National Drinking Water Standards.
Polyphosphate Media (Poly)
Polyphosphate Media is added to mask the effects of high iron concentrations. The Polyphosphate delays the precipitation of oxidized manganese and iron, thereby greatly reducing the layer of scale that forms on the pipes. The effect is called sequestration. The iron or manganese ion is surrounded by a chain of phosphate molecules and is not allowed to precipitate in the water.
Mixed Bed Ion-Exchange DI Resin
The MBD-30 cartridge is a self indicating mixed bed resin. It is a mix of nuclear grade hydrogen and hydroxide form resins. The anion resin is a Type I strongly based gel resin with an indicator dye that changes from blue to colorless as the resin exhausts.
The cation component is a strong acid sulfonated polystyrene gel type cation exchange resin. During exhaustion, as the indicator dye changes color, the appearance of the mixed bed changes from a blue color to Amber.
MBD30 Changes color from Blue to Amber as it exhausts Clear See Through Cartridge for Visual Determination
What is an ion exchange process ?
Ion Exchange is a process that removes detrimental ions from water and replaces them with less damaging ions. In practice ion exchange occurs between water containing ions and an insoluble ion exchange bead with ion exchange properties. Ion exchange can only take place between ions of the same charge namely anions for anions and cations for cations. Anion exchange resins have positively (+) charged exchange sites with anions attached. Cations -exchange resins have negatively (-) charged exchange sites with cations attached. In typical water supplies, the ion exchange resin is more selective for divalent (two positive or negative charges) and trivalent (three positive or negative charges) than monovalent ions. The ion exchange performance is largely dependent on the density of the beads, mechanical resistance, the grain size, the total capacity, break through capacity, porosity of a system, flow, rate, selectivity and the rate of exchange.
Why we have to remove ions ?
The dissolved salts in the natural water pose serious problems for machines and devices that contain, or use water. That is because salts form scales in and/or corrode: pipelines, conduits and tubing. Such also interferes with many chemical processes. In natural water and waste water, there are often undesirable and desirable ions, and some of them may even be worth recovering. But, clearly it is important to remove them when they are present in drinking water.
NOTE: AMPAC CARTRIDGES ARE NOT INTENDED TO BE USED WHERE THE WATER IS MICROBIOLOGICALLY CONTAMINATED, OR WITH WATER OF AN UNKNOWN QUALITY
Home carbon water filter bacteria removal is assured with Wholehouse Carbon Filter AP1500C by AMPAC USA.
View details
Buy Quad Whole House BB UV, BB4-20 from AMPAC USA. We also offer commercial water filters. To buy Quad Whole House BB UV or any other device call 909-548-4900.
View details