What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis, Water Filter Systems - Ampac USA
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Technology is a simple and straightforward water purification process. RO technology has been used since mid 1900's and been used for years to remove contaminants and minerals from water. this technology has also proven to be the most efficient and cost effective process to convert brackish water, well water or seawater to pure drinking water. This technology has been successfully used for Residential, Commercial, Industrial Applications.
The RO process was first described by a Scientist from France in 1748, he noted that water spontaneously diffused through a pig bladder membrane into alcohol. Two Hundred years later, this process was modified and was called reverse osmosis, this RO Process allows people throughout the world to affordably convert non potable water into pure drinking water. RO systems now are everywhere, and can be found providing pure drinking water from the kitchen to installations used in space ships.
Reverse Osmosis (RO)is a technology that is found anywhere pure water is needed; common Reverse Osmosis uses include:
- Human Consumption
- Agriculture
- Humidification
- Ice-Making
- Rinse Waters
- Biomedical Applications
- Laboratory Applications
- Pharmaceutical Production
- Kidney Dialysis
- Water used in chemical processes
- Animal Feed
- Metal Plating Applications
- Wastewater Treatment
- Boiler Water
- Car Battery Water
- Semiconductor production
- Car Wash Water Reclamation
- Photography
- Cosmetics
- Hatcheries
- Restaurants
- Greenhouses
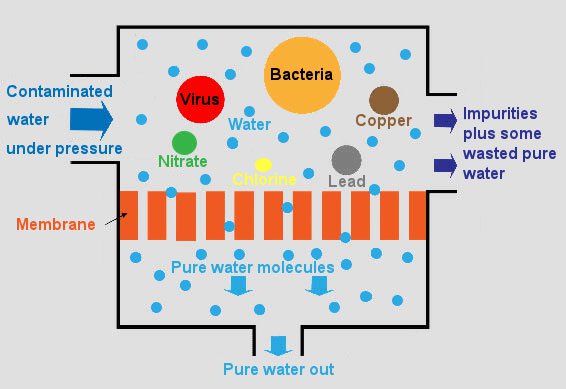
What is a Reverse Osmosis - RO Process?
No matter how bad your water supply may be, a good RO system will get rid of almost all impurities. A typical reverse osmosis system has the most comprehensive decontaminating properties. It works on a straight forward technology which passes untreated water through a semi-permeable membrane that blocks impurities and releases a safe and pure form of water.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Purification Systems.
The osmosis invention process through a semipermeable membrane was first discovered in the late 1700s. Osmosis phenomenon was observed only in laboratories around the world Until mid-1940s. In 1949, researchers in UCLA (University of California Los Angeles) first tested the Osmosis Process to remove salt from seawater ( Seawater Desalination Process) using semipermeable membranes. Researchers finally produced salt-free fresh water from seawater.
Osmosis is a phenomenon that occurs naturally and is one of the most important natural phenomena. Osmosis is a process were water flows from a less concentrated liquid through to a more concentrated liquid through a semipermeable membrane until concentration on both sides is equal, this is the reason why as an example plant roots absorb water from the soil, or water is absorbed from blood to human kidneys.
Reverse Osmosis is reversing the Osmosis phenomenon. Whereas Osmosis occurs naturally, Reverse Osmosis occurs when you apply pressure greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure to the higher saline solution to allow water to travel through a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of water molecules to produce a lower saline solution (Pure Water) separating the majority of contaminants, dissolved solids, salts, organics, bacteria, and pyrogens.
Ampac USA Design and Manufacture Advanced Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Systems. Ampac USA builds standard and Custom RO Systems specifically designed for customers requirements and conditions from Residential, Commercial to Industrial RO Systems, Ampac USA also manufacture Seawater Desalination watermakers, High Purity Laboratory Reagent Type Water Systems, as per Client's Feed Water Analysis, Requirements and Conditions.
Ampac USA conduct comprehensive study to achieve the most efficient solution that can fit your application. Ampac USA study Customers' Analysis and Requirements in extreme details to design the best solution to solve its clients' water problems and needs. Ampac USA Systems Engineers analyze and consult with our skilled design staff to engineer the best solution tailored to fit specific requirements of client's projects. Then Ampac USA Engineers will determine the best water purification solution that will be appropriate for client's water conditions.
How Reverse Osmosis Works:
Reverse Osmosis Working - A semipermeable membrane, like the membrane of a cell wall or a bladder, is selective about what it allows to pass through, and what it prevents from passing. These membranes in general pass water very easily because of its small molecular size; but also prevent many other contaminants from passing by trapping them. Water will typically be present on both sides of the membrane, with each side having a different concentration of dissolved minerals.
Since the water is the less concentrated solution seeks to dilute the more concentrated solution, water will pass through the membrane from the lower concentration side to the greater concentration side. Eventually, osmotic pressure will counter the diffusion process exactly, and an equilibrium will form. So, this is how reverse osmosis works.
Distillation is an Alternative to R/O Water Treatment
Distillation involves boiling the water to produce water vapor. The water vapor then rises to a cooled surface where it can condense back into a liquid and be collected. Because the dissolved solids are not normally vaporized, they remain in the boiling solution. Distillation is one of mankind's earliest forms of water treatment, and it is still a popular treatment solution throughout the world today.
In ancient times, the Greeks used this process on their ships to convert sea water into drinking water. In far-eastern cultures, water was distilled for use in "Ranbiki" tea ceremonies.
Today, distilled water is still used to convert sea water to drinking water on older ships and in arid parts of the world, and to treat water in other areas that are fouled by natural and unnatural contaminants. Distillation is perhaps the one water treatment technology that most completely reduces the widest range of drinking water contaminants.
Not only is distillation one of the most effective forms of treatment, but it is also one of the easiest to understand: untreated water is converted into water vapor, which is then condensed back into liquid form. Most of the contaminants are left behind in the boiling chamber, with the condensed water being virtually contaminant-free. Anyone who has accidentally let a pot of water boil completely out on the stove is familiar with this process and familiar with the crust of contaminants typically left behind after the water is gone.
In nature, this basic process is responsible for the hydrologic cycle. The sun causes water to evaporate from surface sources such as lakes, oceans, and streams. The water vapor eventually comes in contact with cooler air, where it re-condenses to form dew or rain. This process can be imitated artificially, and more rapidly than in nature, using alternative sources of heating and cooling.
Deionization (DI) in Conjunction with RO Water Treatment
Water is passed between a positive electrode and a negative electrode. Ion selective membranes allow the positive ions to separate from the water toward the negative electrode and the negative ions toward the positive electrode. High purity de-ionized water results. The water is usually passed through an RO System first to remove non-ionic organic contaminants.
Deionization (DI) is a water filtration process whereby total dissolved solids (TDS) are removed from water through ion exchange. In simple terms, by controlling the electric charge of ions in the water, it is possible to remove the TDS. Much like a positively charged magnet will attract a negatively charged magnet (and vice-versa), DI resins attract non-water ions and replace them with water ions, leaving a more pure water form.
The process of deionization uses two resins that are opposite in charges – the cat-ionic (negative) and the anionic (positive). The cationic resin is typically made from styrene containing negatively charged sulfonic acid groups and will be pre-charged with hydrogen ions. This resin will attract the positively charged ions in the water (Ca++, Mg++, Na+, etc.) and releases an equivalent amount of hydrogen (H+) ions.
Like the cat-ionic, the anionic resin is also made from styrene, but contains positively charged quaternary ammonium groups, and will be pre-charged with hydroxide ions. This resin will attract the negatively charged ions (HCO3-, Cl-, SO4--, etc.) and releases an equivalent amount of hydroxide (OH-). The hydrogen and hydroxide ions then combine to form water. (H+ + OH- = HOH or H2O.)